According to CyberTechnologyInsights, 81% of organizations have fully or partially implemented a Zero Trust model, with 19% still in the planning phase. Organizations of all sizes are adopting the Zero Trust security model.
The reason is that the traditional “trust but verify” approach no longer works as traditional perimeter-based defenses are insufficient in the times of AI and LLMs. Attackers routinely bypass firewalls, run social engineer attacks, and exploit compromised credentials, misconfigured cloud environments, and vulnerable endpoints to move laterally across networks.
In the last post, we covered implementation roadmap of Zero Securtity model. In this blog post, the various aspect of Zero Trust security model and recommend the open source tools for each part of the process.
What is Zero Trust security model?
Zero Trust is a security approach that treats every user, device, and request as untrusted until proven otherwise. In simple words, Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no one, inside or outside your network, can be trusted by default.
Why use open source tools to implement Zero Trust security?
Zero Trust requires multi-layered controls, and proprietary solutions can be expensive, especially at scale. Open source communities (e.g., CNCF, OWASP) evolve quickly to counter new threats. For Zero Trust, this means faster adoption. So open source tools can accelerate Zero Trust adoption by offering affordability, transparency, flexibility, faster innovation, and compliance support, all without vendor lock-in.
Open source to implement Zero Trust security
The Zero Trust security model is a combination of various best security practices. We’ll cover the best open source tools to use for each process.
1. Verify Explicitly
Verify explicitly means that you should always confirm a user’s identity based on full context (identity, device, location, risk), their device, and the access request using strong authentication before granting entry; there should be no assumptions or shortcuts.
Open source tools to verify explicitly:
- Keycloak → Identity and Access Management (supports SSO, OIDC, SAML, MFA).
- Authelia → Reverse proxy authentication and authorization with 2FA support.
- Dex → OIDC identity service for Kubernetes and microservices.
- FreeIPA → Identity management with LDAP/Kerberos.
When to Choose:
- Small to mid-sized apps → Authelia (lightweight, quick setup).
- Cloud-native microservices → Dex (integrates directly with Kubernetes).
- Enterprise IAM → Keycloak or FreeIPA.
Quick Start:
- Deploy Keycloak via Docker or Kubernetes Helm chart.
- Connect to your directory service (LDAP, Active Directory).
- Enable OIDC and SAML for app integrations.
- Enforce MFA using TOTP or WebAuthn.
2. Use Least Privilege Access
Using Least Privilege Access means giving users and systems only the minimum permissions they need to do their job, nothing more, reducing risk if an account is compromised.
Open source tools to implement least privilege access:
- Open Policy Agent (OPA) – Policy-as-code for APIs, Kubernetes, Terraform.
- Kyverno – Kubernetes-native policy management.
- HashiCorp Vault – Dynamic secrets management.
When to Choose:
- API-level enforcement → OPA.
- Kubernetes workloads → Kyverno.
- Secret rotation and short-lived credentials → Vault.
Quick Start:
- Write OPA policies to enforce role- or attribute-based access.
- Integrate OPA with API gateways or Kubernetes admission controllers.
- Store sensitive credentials in Vault and issue dynamic short-lived tokens.
3. Assume Breach
Assume breach means always operating as if an attacker is already inside your network, so defenses are built to limit damage, detect threats quickly, and recover quickly. Design for resilience by limiting lateral movement and detecting anomalies.
Open-Source Options to follow Assume Brach policy:
- Wazuh – Open-source SIEM and threat detection.
- Suricata – IDS/IPS for network traffic analysis.
- TheHive + Cortex – Incident response and threat analysis platform.
- MITRE Caldera – Adversary emulation for breach simulation.
When to Choose:
- Real-time detection → Suricata + Wazuh.
- Incident handling → TheHive + Cortex.
- Breach simulations → MITRE Caldera.
Quick Start:
- Deploy Suricata to monitor inbound/outbound network traffic.
- Forward alerts to Wazuh for correlation.
- Simulate breaches quarterly using Caldera to validate detection.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Validation
Continuous Monitoring and Validation means constantly checking user behavior, device health, and network activity in real time to ensure trust is never permanent and threats are caught early.
Open-Source Options to continuously monitor and validate:
- Prometheus + Grafana – Metrics collection and visualization.
- Falco – Runtime security for containers and Kubernetes
- ELK/OpenSearch – Centralized logging.
- Zeek – Deep network monitoring and protocol analysis.
When to Choose:
- Container runtime → Falco.
- Network-level anomalies → Zeek.
- Full observability stack → ELK/OpenSearch + Grafana.
Quick Start:
- Deploy Falco in your Kubernetes clusters.
- Stream logs to OpenSearch for central analysis.
- Build Grafana dashboards with real-time anomaly alerts.
5. Device Access Control
Device Access Control means only allowing trusted, secure, and compliant devices to connect to your network, reducing the risk of compromised or unmanaged devices gaining access.
Open-Source Options for Device Access Control:
- osquery – Query endpoint state using SQL-like syntax.
- Kolide Fleet – Central management for osquery agents.
- Wazuh – Device posture checks.
When to Choose:
- Endpoint visibility and compliance checks → osquery (lightweight agent, versatile queries).
- Centralized management at scale → Kolide Fleet (manage 100s–1000s of endpoints).
- Integrated security posture monitoring → Wazuh (combine device health with SIEM).
Quick Start:
- Install osquery on all endpoints.
- Use Kolide Fleet to enforce compliance policies.
- Integrate compliance checks into VPN or network access gateways.
6. Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation means breaking your network into smaller, isolated zones so that even if attackers get in, their movement is limited and contained. Restrict access between workloads to prevent lateral movement.
Open-Source Options to Implement Microsegmentation:
- Cilium – eBPF-based networking and security for Kubernetes.
- Istio – Service mesh with mTLS.
- Calico – Kubernetes network policies.
- Envoy – Service-to-service proxy.
When to Choose:
- Cloud-native Kubernetes workloads → Cilium (eBPF-based, scalable, fine-grained control).
- Service-to-service encryption & policy enforcement → Istio (mTLS, advanced service mesh).
- Lightweight Kubernetes network security → Calico (simpler network policy enforcement).
- Standalone service communication proxy → Envoy (service-to-service mTLS outside service mesh).
Quick Start:
- Deploy Cilium or Istio in Kubernetes.
- Enforce mTLS between workloads.
- Segment workloads by namespace or label.
7. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) means requiring users to prove their identity with more than one factor, like a password plus a phone code, so that stolen credentials alone can’t grant access.
Open-Source Options for Multi-Factor Authentication:
- Keycloak MFA – Built-in TOTP/WebAuthn.
- PrivacyIDEA – Centralized MFA for enterprise.
- Authelia – MFA for web apps.
When to Choose:
- Web/mobile applications with SSO → Keycloak MFA (built-in, integrates with OIDC/SAML).
- Enterprise-wide MFA across systems → PrivacyIDEA (flexible token support, enterprise-grade).
- Simple web app protection → Authelia (lightweight, integrates easily with reverse proxies).
Quick Start:
- Choose an MFA method (TOTP, FIDO2, SMS).
- Integrate with an SSO/IAM provider.
- Enforce MFA for all admin and privileged accounts first.
Quick reference table for each phase:
| Principle | One-Line Definition | Open-Source Tools |
| Verify Explicitly | Always authenticate and authorize users and devices based on full context, not assumptions. | Keycloak, Authelia, Dex, FreeIPA |
| Use Least Privilege Access | Grant users and systems only the minimum permissions required to perform their tasks. | Open Policy Agent (OPA), Kyverno, HashiCorp Vault |
| Assume Breach | Design systems as if an attacker is already inside, limiting lateral movement and ensuring resilience. | Wazuh, Suricata, TheHive + Cortex, MITRE Caldera |
| Continuous Monitoring and Validation | Continuously observe user, device, and system behavior to validate trust in real time. | Prometheus + Grafana, Falco, ELK/OpenSearch, Zeek |
| Device Access Control | Ensure only trusted and compliant devices are granted access to corporate resources. | osquery, Kolide Fleet, Wazuh |
| Microsegmentation | Divide networks and workloads into isolated zones to minimize attack surface and lateral movement. | Cilium, Istio, Calico, Envoy |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Require two or more authentication factors to verify user identity before granting access. | Keycloak MFA, PrivacyIDEA, Authelia |
Open-Source Zero Trust Reference Architecture
This Open-Source Zero Trust Reference Architecture illustrates a layered security approach that enforces “never trust, always verify” principles using cost-effective, community-driven tools.
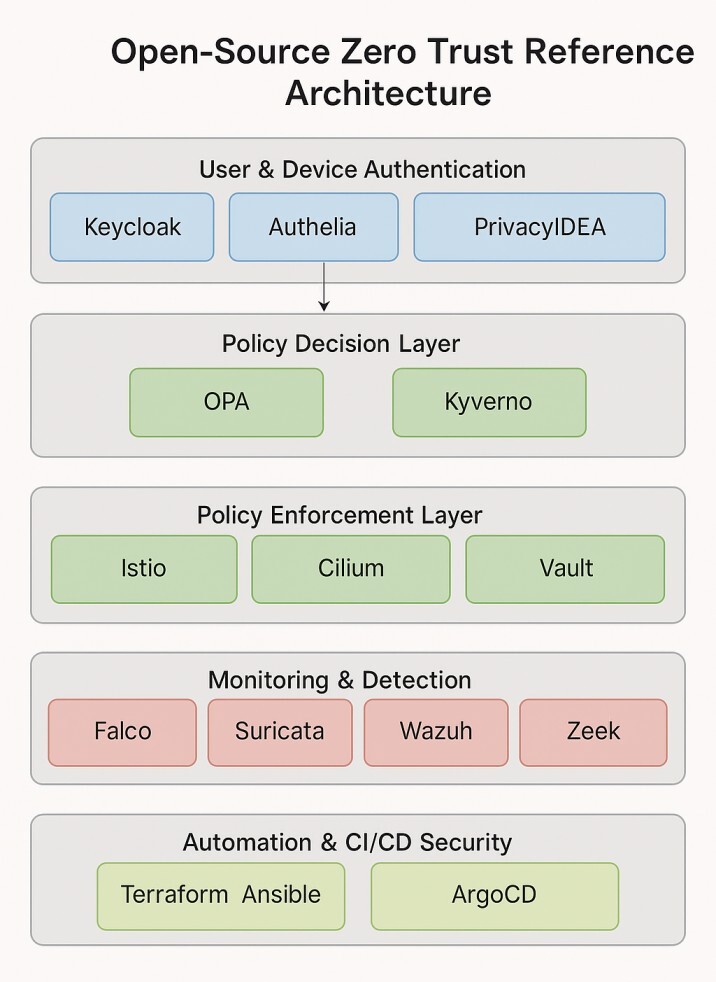
Automation & Deployment
To make this Zero Trust stack scalable, we can use:
- Terraform / Ansible → Deploy policies and infrastructure as code.
- GitOps (ArgoCD / Flux) → Manage Kubernetes Zero Trust configurations.
- CI/CD Security Gates → OPA/Kyverno checks in pipelines.
Final words
Zero Trust is no longer optional; it’s the baseline for modern cybersecurity. The open-source ecosystem offers everything you need to implement Zero Trust without costly vendor lock-in.
However, choosing, implementing, and managing OSS tools can be complicated in practice. At OffloadSecurity, we help organizations design, deploy, and automate Zero Trust architectures using battle-tested open-source tools.
Whether you’re starting from scratch or enhancing an existing security posture, we can guide you from strategy to implementation. Contact OffloadSecurity experts for a free Zero Trust readiness assessment.